If you’re interested in astrophysics or anything related to chaos and disorder on systems, you probably have heard about entropy. Entropy is why our universe has disorder and randomness. The increase or decrease of entropy can make a big difference on our universe, lives, and even the most simple things such as a shattered glass, but what is the opposite of entropy? Does it exist, and if it does, what does it do, and what does it bring?
In the world of physics and thermodynamics, entropy is a term that we use for describing the measure of disorder or randomness in a system. The opposite of this concept is Negentropy. The physics world decsribe negentropy as the opposite of entropy. We often overlook this concept and don’t really think of much. In essence, negentropy represents a system’s measure of order or organization.
In this blog post, we will delve deep into the concept of Negentropy, explain what entropy’s opposite term, understand its definition, key characteristics, and significance in various systems. We will also explore the differences between entropy and negative entropy and how they affect the universe’s behavior.
Defining The Opposite of Entropy. Negentropy
Negentropy, also known as negative entropy or syntropy, is a concept that represents the measure of order, organization, and information within a system. In contrast to entropy, which quantifies the degree of disorder or randomness, Negentropy reflects the presence of structure and coherence.
Basically, Negentropy is entropy’s opposite and serves as a counterbalance to the natural tendency towards disorder. With the existence of Negentropy in the universe, there is a balance between disorder and order.
What is Negentropy?
Negentropy, a term coined by Erwin Schrödinger in his book “What is Life?” published in 1944, stems from the Greek word “negation” and “entropy.” It refers to the negation or reversal of entropy and represents the capacity of a system to counteract the natural tendency towards disorder.
In simpler terms, Negentropy describes the process of creating and maintaining order, structure, and complexity within a system. It encompasses the idea of organization, information storage, and energy utilization to sustain and enhance the system’s overall coherence.
Key Characteristics of Negentropy
To further grasp the concept of Negentropy, let’s explore its fundamental characteristics.
- Order and Organization. Negentropy signifies the presence of order and organization in a system. It indicates the arrangement and coherence of components within the system, leading to a structured and predictable behavior.
- Information Storage and Processing. Negentropy involves the storage and processing of information within a system. It represents the ability to encode, retrieve, and utilize information to enhance the system’s efficiency and functionality.
- Energy Utilization. Negentropy relies on the efficient utilization of energy within a system. It emphasizes the transformation and utilization of energy to maintain and enhance the system’s order and organization.
- Complexity and Adaptability. Negentropy is associated with complexity and adaptability. It involves the development of intricate structures and mechanisms that allow the system to adapt, evolve, and respond to changes in its environment.
- Non-equilibrium State. Negentropy is often observed in systems that are in a non-equilibrium state. This means that the system is not at its maximum entropy or complete randomness but rather maintains a degree of order and structure.
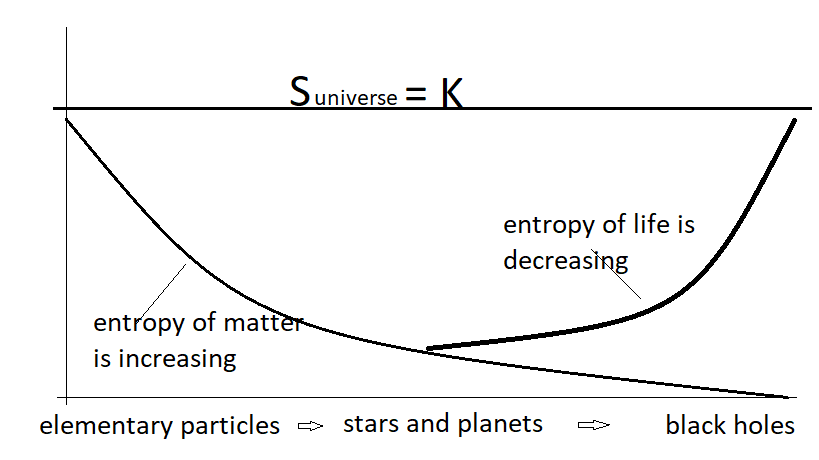
Understanding Entropy. The Measure of Disorder
Entropy is one of the fundamental concepts in thermodynamics and statistical mechanics that quantifies the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It provides a measure of the system’s microscopic configurations and their associated probabilities. To fully comprehend the concept of Negentropy, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of entropy and how it operates in various systems.
What is Entropy?
We can say that entropy is a measure of the number of possible arrangements or states of a system that are consistent with its macroscopic properties, such as energy and volume. It reflects the level of uncertainty or randomness in the system’s microscopic details.
In simpler terms, it is a measure of how many different ways the particles or components of a system can be arranged without affecting its macroscopic properties. A highly ordered system will have low entropy, while a highly disordered or random system will have high entropy.
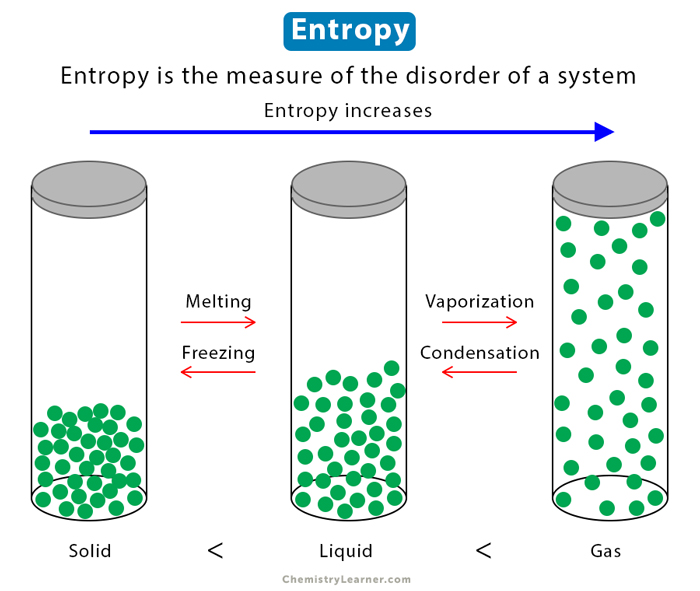
Key Characteristics of Entropy
- Disorder and Randomness. We define a system’s level of disorder or randomness by calculating the entropy’s quantity. It quantifies the extent to which the particles or components of the system are arranged in a disordered manner. The higher it is, the more chaos or disorder there will be within a system.
- Probability and Microstate Configurations. It is also related to the number of possible microstate configurations that a system can have while exhibiting the same macroscopic properties. It is in parallel to the logarithm of the number of microstate configurations.
- Thermodynamic State Function. This concept is also a state function in thermodynamics, meaning that its value depends solely on the system’s current state and not on the path taken to reach that state. It allows for the comparison between different equilibrium states.
- Increase in Entropy. According to the second law of thermodynamics, the isolated system’s entropy generally increases over time. This principle is known as the law of entropy increase. This means that a system’s disorder always increases except for very rare times where it might decrease but it will pick up again. That is a whole different thing which I will not go into now.
- Equilibrium and Maximum Entropy. An equilibrium system means the final position of a system, it represents the most chaotic position of a system. This means that at equilibrium state, a system reaches maximum entropy. This means that the system has achieved the highest level of disorder or randomness possible.
Negentropy vs Entropy: A Comparative Study
As we mentioned, These two terms are two very different concepts that counterbalance themselves. So basically, one’s presence in a system balances the other one’s presence in the same system. Negentropy is generally the thing that balances entropy’s disorder. Understanding the difference between the two allows us to have a deeper insight into the dynamics of order and disorder within various domains.
Contrasting Definitions
As I mentioned, these terms define two opposite concepts that represent different aspects of order and disorder within a system. While entropy measures the degree of disorder or randomness, Negentropy quantifies the level of order, organization, and information.
Entropy signifies how willing a system is to move towards maximum disorder or randomness. It quantifies the number of possible arrangements or microstate configurations that are consistent with the system’s macroscopic properties. In other words, entropy reflects the system’s potential to explore different configurations while maintaining its overall macroscopic properties.
On the other hand, Negentropy represents the system’s ability to counteract the natural tendency towards disorder. It reflects the presence of order, organization, and information within the system, indicating a state of reduced randomness. Negentropy signifies the system’s capacity to maintain and enhance its structure, complexity, and coherence.
How Negentropy and Entropy Affect Systems
Both of these terms have profound effects on the behavior and dynamics of different systems. The interplay between these two concepts determines the overall state and evolution of the system. Neither of them can’t actually increase or decrease all the time. They have to balance each other, which they generally do according to the nature of law. We see it on our studies of the universe that entropy’s increase is generally not all the time, sometimes it stops and balances itself with negentropy.
Entropy tends to increase over time in isolated systems, as the second law of thermodynamics states. This increase leads to a higher degree of disorder and randomness. In contrast, Negentropy represents the counteracting force that resists this increase in disorder. It allows for the preservation and generation of order, organization, and complexity within the system.
Systems that exhibit high Negentropy are characterized by their ability to maintain and enhance their structure and coherence. They can utilize energy efficiently, store and process information, and adapt to changes in their environment. These systems are often in a non-equilibrium state, where there is a continuous flow of energy and matter that sustains their negentropic behavior.
Examples of Negentropy and Entropy in Real-world Scenarios
Let’s consider some real-world scenarios.
Biological Systems
Living organisms rely on Negentropy to maintain their structure and functionality. They utilize energy to counteract the natural tendency towards disorder and perform complex processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Entropy, on the other hand, is associated with aging and degradation, as biological systems eventually succumb to entropy’s effects.
Information Theory
In information theory, Negentropy represents the amount of information that can be extracted from a system. It reflects the level of order and structure in the information. When we look at entropy in information, it’s increase quantifies the uncertainty or randomness in the information. Efficient coding and compression techniques aim to reduce entropy and increase Negentropy in information systems.
Technological Innovations
Negentropy plays a crucial role in technological advancements. For example, engineers and scientists strive to design energy-efficient systems that minimize the entropy’s effects and maximize Negentropy. This allows for the development of more efficient electronic devices, communication networks, and renewable energy technologies.
Applications of Negentropy and Entropy in Science and Technology
How do we use these two terms in science and technology, especially negentropy since entropy always increases everywhere and leads to changes? Are there any use cases that can affect our research toward understanding the universe? Tough questions about valid ones.
Negentropy in Information Theory
In the realm of information theory, Negentropy finds applications in data compression, error correction, and efficient data storage. By reducing the entropy of information, such as through compression algorithms, we can increase the Negentropy and improve the data transmission and storage systems’ efficiency. Error-correcting codes also utilize negentropy principles to ensure reliable communication and minimize information loss.
Entropy in Thermodynamics
Entropy is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, where it has a crucial role in understanding the behavior of energy and heat transfer. The second law of thermodynamics says that an isolated system’s entropy tends to increase over time. This principle guides the design and optimization of energy conversion systems, such as heat engines, refrigeration cycles, and power plants. Maximizing the conversion efficiency while minimizing entropy generation is a key objective in these applications.
Utilizing Negentropy and Entropy in Technological Innovation
As I mentioned above, scienticsts and engineers use these two things side by side in the innovations. They don’t directly put them in the things they innovate but they make sure that systems will work in parallel.
- Renewable Energy Systems. Negentropy principles guide the design and optimization of important renewable energy options, like solar panels and wind turbines. These systems aim to harness and convert energy efficiently while minimizing entropy generation.
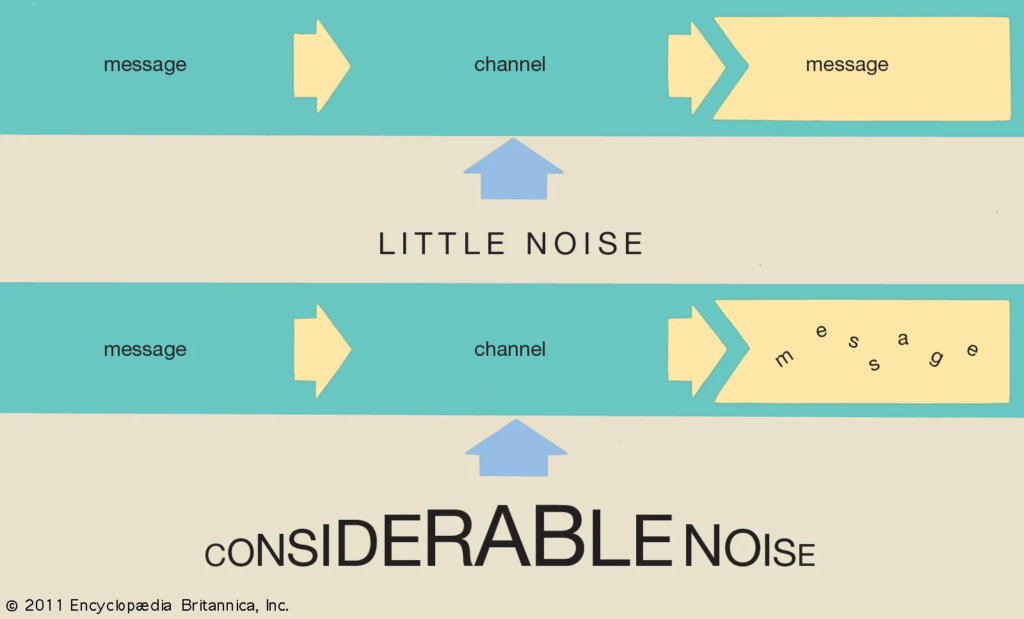
- Communication Networks. In telecommunications, we use negentropy principles to improve the efficiency and reliability of data transmission. Error correction coding, modulation schemes, and other similar techniques help increase the Negentropy of transmitted signals. This reduces the impact of noise and improves the overall quality of communication.
- Biotechnology and Medicine. Understanding the principles of Negentropy and entropy is crucial in the fields of biotechnology and medicine. Researchers utilize these concepts to study biological systems, develop advanced drug delivery systems, and optimize medical treatments. The goal is to enhance the negentropic aspects of biological processes while minimizing the effects of entropy-related degradation.
- Complex Systems and Artificial Intelligence. Negentropy and entropy concepts are also applied in the study of complex systems and artificial intelligence. Researchers aim to develop algorithms and models that exhibit high Negentropy, allowing for the emergence of complex and intelligent behaviors. This includes applications in machine learning, neural networks, and evolutionary algorithms.
Conclusion
What is the opposite of entropy is Negentropy. It is the counterbalance to entropy and epitomizes the essence of order, structure, and information within a system. Its opposition to entropy signifies a crucial equilibrium, maintaining a balance between disorder and organization in the universe.
Defined as the reversal of entropy, Negentropy reflects a system’s ability to counteract the relentless march toward disorder. This concept embodies organization, information storage, energy utilization, and adaptability, fostering a non-equilibrium state that sustains structure amidst potential chaos.
In contrast, entropy symbolizes the natural progression toward disorder, quantifying randomness and uncertainty within a system. Its increase over time in isolated systems accentuates disorder, contrasting with the efforts of Negentropy to uphold coherence and complexity.
The distinctions between Negentropy and entropy delineate their impact on diverse systems. From biological organisms relying on Negentropy for functionality to information theory applications minimizing entropy for efficient data transmission, these concepts shape technological innovations and scientific pursuits.
Negentropy finds application in data compression, error correction, and renewable energy systems, while entropy remains fundamental in understanding thermodynamic behavior, aiding in energy conversion and optimization.
Ultimately, the interplay between Negentropy and entropy dictates the evolution and functionality of systems across various domains. As we harness these principles in science and technology, their balance offers insights into the intricacies of the universe, guiding innovations and advancements that navigate the delicate equilibrium between disorder and order.