The universe is a vast and mysterious place, filled with countless galaxies, stars, and planets. For centuries, humans have been fascinated by the study of the cosmos, seeking to unravel its secrets and understand our place within it. This field of study is known as cosmology.
Cosmology stands as one of the most important fields of study to understand more about us, whether we are alone, and the structure of the universe from a holistic view. That’s why if you are interested in astronomy, you should also know what cosmology is and how it came to be.
In this article, we’ll take a deep look at cosmology, explain what is cosmology, and provide you with an introduction to the study of the universe. We will delve into the history of cosmology, from ancient beliefs to the birth of modern cosmology and the key figures who have shaped our understanding of the cosmos.
What is Cosmology?
Cosmology is the study of our universe with scientific approaches, including its origin, structure, and evolution. It is a field that combines principles from physics, astronomy, mathematics, and philosophy to understand the fundamental nature of the cosmos.
At its core, cosmology seeks to answer some of the most important questions about the universe’s existence. Where did the universe come from? How did it evolve over time? What is its fate? These are just a few of the inquiries that cosmologists strive to address.
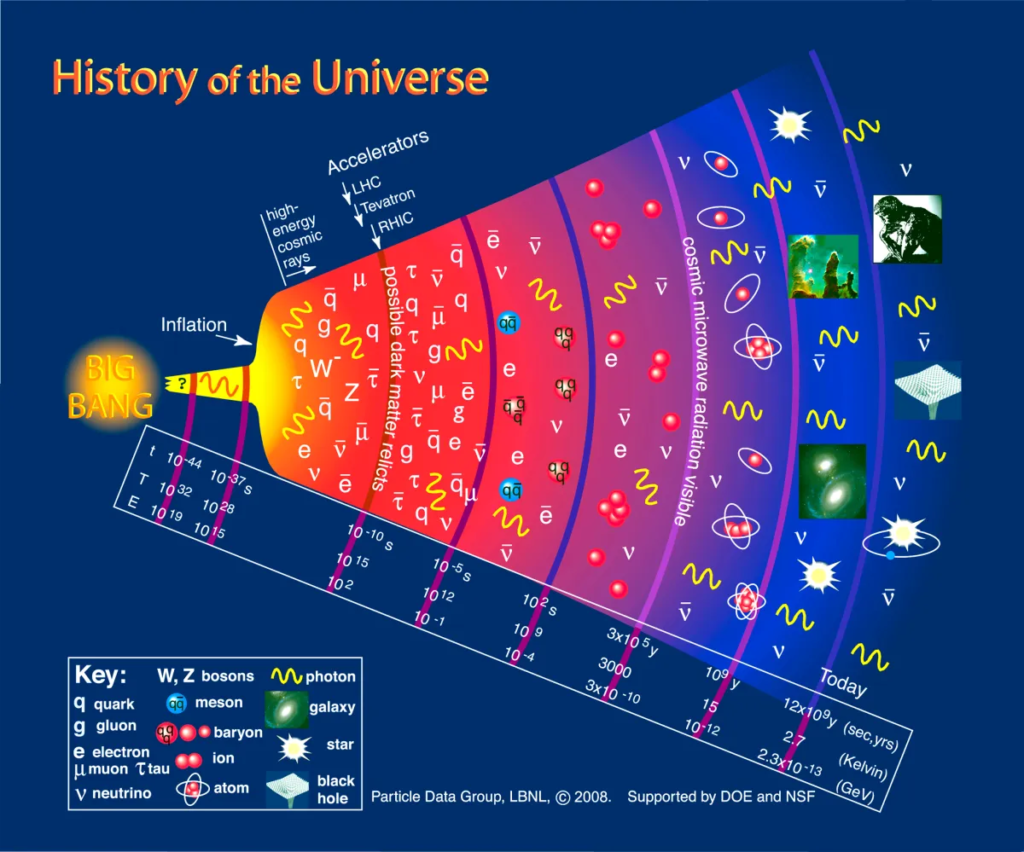
Cosmology goes beyond the study of individual celestial objects like stars and galaxies. Instead, it focuses on understanding the universe as a unified system, investigating its overall properties, dynamics, and interactions. By examining the large-scale structure and behavior of the cosmos, cosmologists aim to uncover the underlying principles that govern its existence.
Modern cosmology is driven by observation, experimentation, and applying mathematical and computational techniques to analyze and interpret data.
Cosmologists use various tools and technologies to gather information about the universe. Observational astronomy plays a crucial role, where scientists use telescopes and similar instruments to observe celestial objects and collect data on their properties, such as their distance, composition, and motion. Additionally, theoretical and computational cosmology allows scientists to develop mathematical models and simulations to study the universe’s behavior and predict its past, present, and future.
By studying cosmology, we gain insights into the fundamental laws of physics, the nature of matter and energy, and the forces that shape the universe. It helps us comprehend the vastness and complexity of the cosmos. It provides a framework for understanding our place within it.
The History of Cosmology
Throughout history, different cultures and civilizations have developed their own cosmological beliefs and explanations for the origin and nature of the universe. These ancient cosmologies often involved mythological or religious narratives that sought to provide meaning and understanding of the cosmos.
However, over time, cosmology has changed and adapted to its time’s society with more modern thoughts and technologies. This affected the study of cosmology. We also still sometimes use some of the findings from older times as they were practically true. So, the history of cosmology is not just a piece of history. It also defines the bedrock of today’s cosmology in some parts.
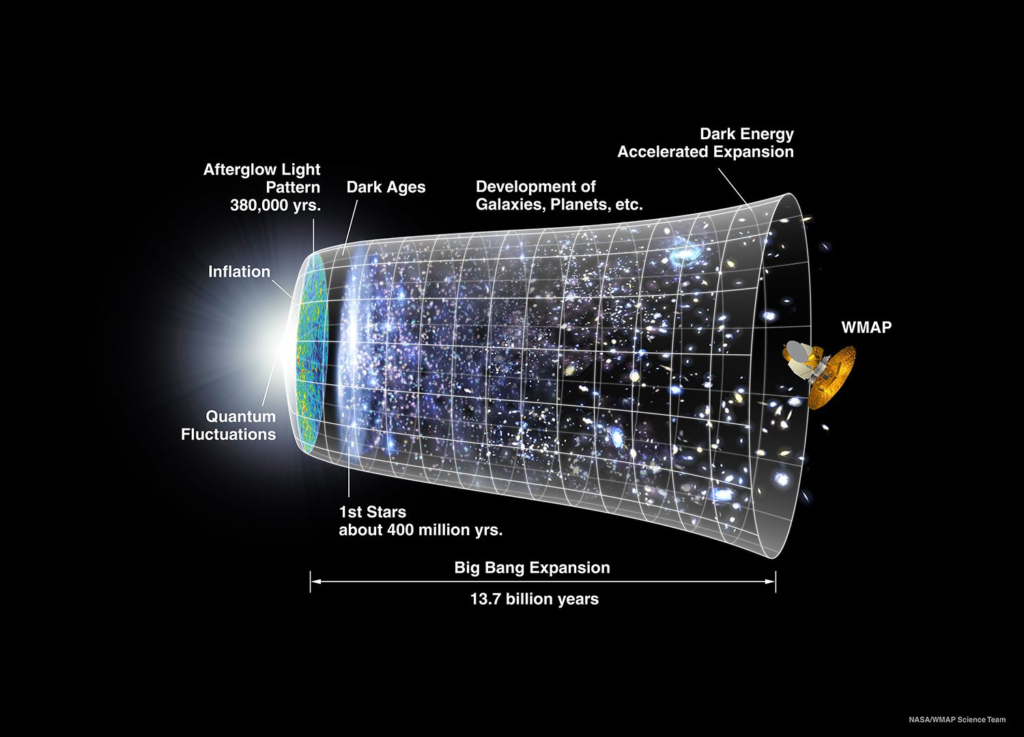
Ancient Cosmological Beliefs
In ancient times, various cultures developed their own cosmological beliefs to explain the origin and nature of the universe. These beliefs are often intertwined with mythology, religion, and philosophical ideas.
Egyptian Cosmology
The ancient Egyptians believed in a cosmology centered around the concept of Ma’at, the balance and order of the universe. They believed that the world appeared from the primordial waters of chaos and that the sun god Ra played a central role in creating and sustaining the cosmos.
Mesopotamian Cosmology
In Mesopotamia, the Babylonians and Assyrians developed cosmological beliefs that involved a flat Earth surrounded by a solid dome-like sky, which held the stars and planets. They also believed in various celestial deities and associated them with specific celestial bodies.
Ancient Greek Cosmology
The ancient Greeks were pioneers in developing cosmological theories based on observation and reason. Prominent Greek philosophers, such as Pythagoras, Aristotle, and Plato, proposed different universe models. One of these was the geocentric model that thought the Earth was at the center of the universe. The other crucial one was the heliocentric model, which placed the Sun at the center.
The Birth of Modern Cosmology
The birth of modern cosmology can be traced back to the scientific revolution that took place during the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods. Modern cosmology helped us to understand the universe in a more structured way with proof and better understanding.
Copernican Revolution
In the 16th century, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the heliocentric model, challenging the prevailing geocentric view. His work laid the foundation for a new understanding of the solar system. It paved the way for future advancements in cosmology.
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
Johannes Kepler created three fundamental laws that describe the planets’ motion around the sun in the early 17th century. These laws provided crucial insights into celestial bodies’ dynamics and contributed to the development of modern cosmology.
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Isaac Newton’s discovery of the law of universal gravitation in the late 17th century revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics. It allowed scientists to explain the motion of cosmic bodies and laid the groundwork for future advancements in cosmology.

Key Figures in Cosmological History
Throughout history, several key figures have made significant contributions to the field of cosmology. Some notable individuals include:
- Albert Einstein. Einstein’s general relativity theory, which was published in 1915, provided a new framework for understanding gravity and the behavior of massive objects in the universe. It revolutionized cosmology and led to the concept of an expanding universe.
- Edwin Hubble. In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble made groundbreaking observations that demonstrated the existence of galaxies beyond the Milky Way and provided evidence for the universe’s expansion. Hubble’s work laid the foundation for the Big Bang theory.
- Georges Lemaître. Lemaître, a Belgian physicist and Catholic priest, proposed the idea of an expanding universe and formulated the concept of the Big Bang in the 1920s. His work was instrumental in establishing the modern understanding of the origin of the universe.
Key Concepts in Cosmology
Cosmology encompasses a wide range of fascinating concepts that help us understand the nature and workings of the universe. The fundamental ideas and theories in cosmology are what created the foundation for cosmology. These include the Big Bang theory, dark matter and dark energy, cosmic microwave background radiation, and the expanding universe.
The Big Bang Theory
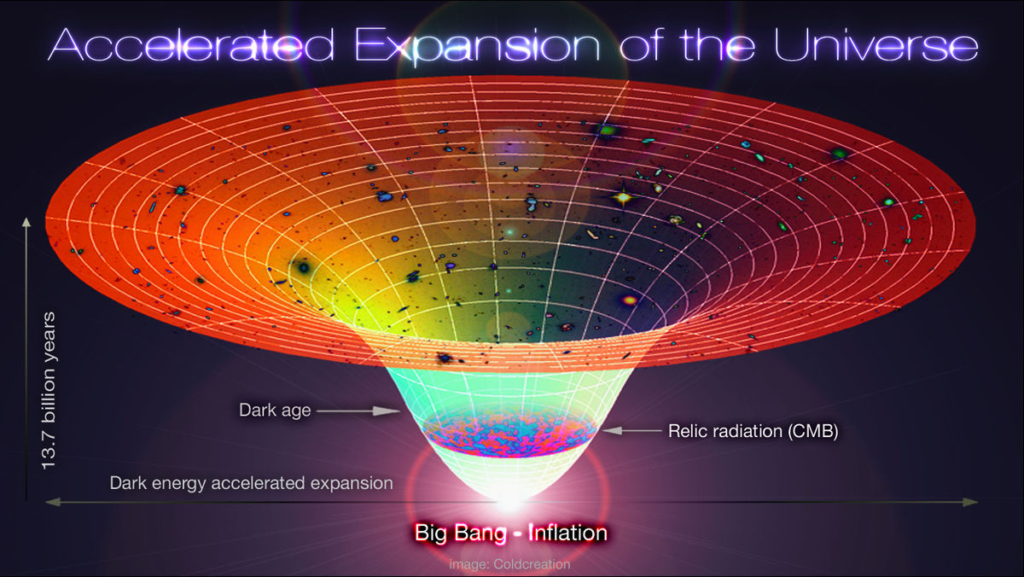
The Big Bang theory is a fundamental cosmological model explaining the birth of the universe. It describes the origin and evolution of the universe. According to the Big Bang, the universe began as an extremely hot and dense singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago. It then underwent rapid expansion, cooling down and giving rise to the formation of matter and energy.
The Big Bang theory gives us an explanation for a variety of cosmological phenomena. Some of these are the cosmic microwave background radiation, the observed distribution of galaxies, and the excess light elements. It also suggests that the universe continues to expand to this day.
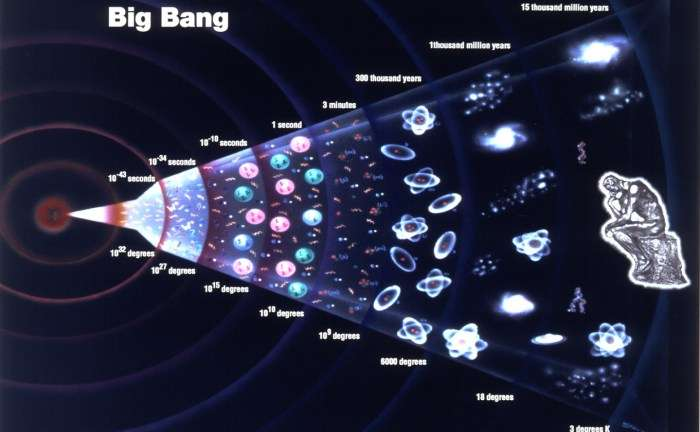
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Dark matter and dark energy are two of the most mysterious components that exist in our universe. These two matters make up a significant portion of the universe, yet their exact nature remains largely unknown.
Dark matter is a form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation, making it invisible to direct detection. We infer the presence of this matter by its gravitational effects on visible matter and how it affects the structure of the universe. Dark matter has a vital role in the formation and evolution of galaxies and is believed to outweigh visible matter by approximately six times.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is an even more enigmatic concept. This energy is a hypothetical energy form that exists in the entire universe. It is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe that we can see. Unlike dark matter, which attracts matter through gravity, dark energy is thought to possess repulsive gravitational effects, causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) is a faint, uniform radiation that permeates the entire universe. It is considered to be a remnant of the early stages of the universe, specifically the era when it transitioned from being opaque to becoming transparent, known as recombination.
The discovery of the CMB in 1965 provided strong evidence in support of the Big Bang theory. The CMB is essentially the afterglow of the Big Bang, and its precise measurement has allowed cosmologists to gain insights into the composition, age, and geometry of the universe. I’ve written a very detailed article about cosmic microwave background radiation and its definition.
The Expanding Universe
Observational evidence, such as the redshift of galaxies, points to the fact that the universe is expanding. The concept of an expanding universe is a cornerstone of modern cosmology and is closely tied to the Big Bang theory.
The expansion of the universe suggests that galaxies and other cosmic structures are moving away from each other as space itself expands. This means that the universe was denser and hotter in the past, and as it expands, it cools down and becomes less dense.
The expanding universe has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the cosmos, including the ultimate fate of the universe and the concept of cosmic inflation. It suggests that the universe experienced a time of extreme expansion right after the Big Bang.
Tools and Techniques Used in Cosmology
The study of cosmology relies on a variety of tools and special techniques that enable scientists to observe, analyze, and interpret the vast and complex universe. These techniques especially allow us to differentiate the type of cosmology, better follow trends, and come up with new findings.
Observational Astronomy
Observational astronomy is a fundamental tool in cosmology. It involves the direct observation and measurement of celestial objects and phenomena to gather data and insights about the universe. Astronomers use a variety of instruments and techniques for observation.
- Telescopes. Telescopes are essential tools in astronomy, allowing scientists to collect and focus light from any distant object. They can be ground-based or space-based and come in various types, including optical, radio, and X-ray telescopes.
- Spectroscopy. Spectroscopy is the study of how light interacts with matter. By analyzing the spectrum of light emitted or absorbed by cosmic objects, astronomers can determine their composition, temperature, and motion.
- Photometry. Photometry involves measuring the intensity of light emitted by celestial objects. It helps astronomers determine the brightness, color, and variability of stars, galaxies, and other cosmic sources.
- Imaging. Imaging techniques capture detailed images of celestial objects, providing valuable insights into their structure, morphology, and evolution. Advanced imaging technologies, such as adaptive optics and interferometry, enhance the resolution and clarity of astronomical images.
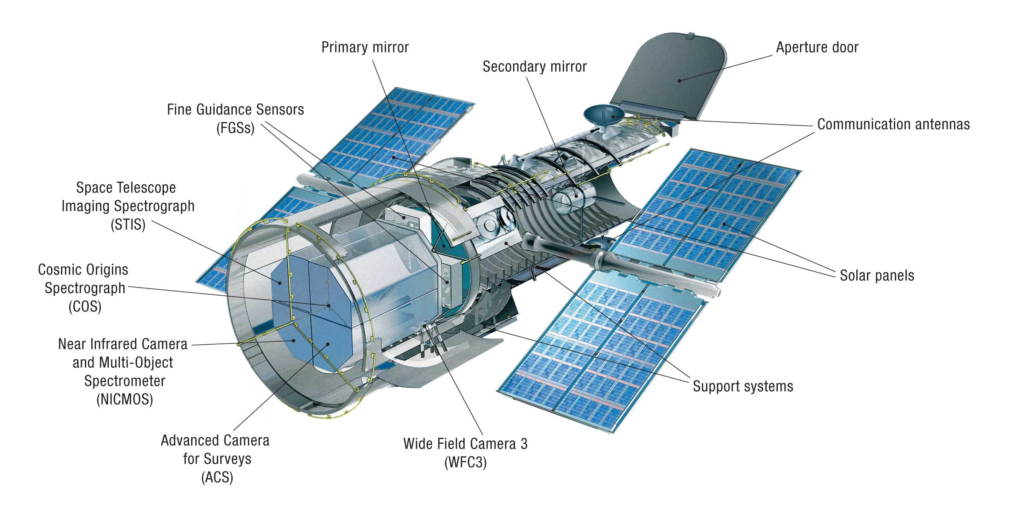
The Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) has massively changed our understanding of the universe since it was launched in 1990. Positioned above Earth’s atmosphere, the HST provides exceptionally clear and detailed images, free from the distortion caused by atmospheric turbulence. Some of the key contributions of the HST to cosmology include:
- Deep Field Observations. The HST’s deep field observations have captured images of some of the most distant and ancient galaxies, shedding light on the early stages of the universe and its evolution.
- Measurement of Cosmic Expansion. The HST played a crucial role in measuring the rate of cosmic expansion, which we know as the Hubble constant. It helps determine the age and size of the universe.
- Study of Dark Matter and Dark Energy. The HST has contributed to our understanding of dark matter and dark energy by observing the gravitational lensing effect caused by the bending of light around massive objects.
Theoretical and Computational Cosmology
Theoretical and computational cosmology involves the development of mathematical models, simulations, and computational techniques to study the universe’s behavior and predict its properties. These tools help cosmologists:
- Formulate and Test Hypotheses. Theoretical models allow cosmologists to propose and test hypotheses about the origin, evolution, and properties of the universe. They help refine our understanding and guide observational and experimental efforts.
- Simulate Cosmic Structures. Computational cosmology enables scientists to simulate the formation and evolution of cosmic structures. These include galaxies and galaxy clusters based on known physical laws. These simulations help validate theories and provide insights into complex processes.
- Analyze Large Datasets. In the era of big data, cosmologists rely on computational techniques to analyze vast amounts of observational data. These methods help identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data, leading to new discoveries and insights.
The combination of observational astronomy, space-based telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope, and theoretical and computational methods has greatly changed our look at the universe.
The Future of Cosmology
Cosmology is an ever-evolving field, constantly pushing the boundaries of our knowledge about the universe.
Unsolved Mysteries in Cosmology
While significant progress has been made in understanding the universe, there are still many unsolved mysteries that intrigue cosmologists. In addition to the work cosmologists do, we mainly try to solve these mysteries.
- Nature of Dark Matter and Dark Energy. Despite their significant influence on the universe, the exact nature of dark matter and dark energy remains elusive. Understanding their composition and properties is one of the key challenges in cosmology.
- Cosmic Inflation. The concept of cosmic inflation suggests that the universe underwent a period of rapid expansion shortly after the Big Bang. However, the precise mechanisms and physical processes that drove inflation are still not fully understood.
- Origin of Cosmic Structures. The formation and evolution of the galaxies in the entire universe, galaxy clusters, and other cosmic structures are still complex and barely understood. Exploring the origin of these structures and the forces that shaped them is an ongoing area of research.
Potential Implications for our Understanding of the Universe
Advancements in cosmology have far-reaching implications beyond the realm of science. Here are a few potential implications that our expanding knowledge of the universe may have.
- Technological Innovations. Cosmology often drives technological advancements. Technologies developed for space missions, such as imaging and data analysis techniques, have practical applications in various fields, from medicine to communications.
- Philosophical and Existential Insights. Our evolving understanding of the universe prompts profound philosophical and existential questions. It challenges our perspectives on our place in the cosmos and the nature of reality, stimulating philosophical and existential contemplation.
As cosmology continues to progress, new discoveries, technologies, and insights will reshape our understanding of the universe and our place within it. The future of cosmology holds immense potential for expanding human knowledge and deepening our understanding of the mysteries that lie beyond our world.
Conclusion
Cosmology is the bedrock of the study of the universe that encompasses almost all other scientific branches that study the cosmos, like astronomy, astrophysics, and so on. From ancient times to our modern days, cosmology has always been there with us. Even though we were able to solve some of the questions, there are still many that are unanswered.
Cosmology continues to be one of the most exciting and dynamic fields of scientific exploration. It helps us to focus on the mysteries of the cosmos and humankind’s place within it. Through continued research, observation, and theoretical advancements, we will continue to unravel the secrets of the universe and gain deeper insights into the nature of existence itself.